Core Principles of the U.S. Constitution
The U.S. Constitution is more than a legal document — it is a framework built on carefully chosen principles designed to prevent tyranny while allowing government to function.
These principles shape every law, court decision, and political debate in the United States. Understanding them is essential to understanding how American government works.
🧱 The Foundation of Constitutional Government
The Constitution rests on a small number of core ideas. Together, they ensure that power is:
-
Legitimate
-
Limited
-
Accountable
-
Divided
Each principle reinforces the others. Remove one, and the system weakens.
🗳️ Popular Sovereignty
Power Comes From the People
The Constitution begins with three powerful words:
“We the People…”
This phrase establishes that government authority flows from the citizens, not from kings, elites, or institutions.
Why It Matters
-
Citizens consent to be governed
-
Elections legitimize power
-
Government serves the public, not itself
A government that ignores the will of the people loses its legitimacy.
🚧 Limited Government
Government Has Boundaries
Under the Constitution, government may only do what it is authorized to do.
Limits come from:
-
The Constitution itself
-
Enumerated powers
-
Individual rights
Why It Matters
Without limits, power inevitably expands. The Constitution exists to restrain authority, not enable abuse.
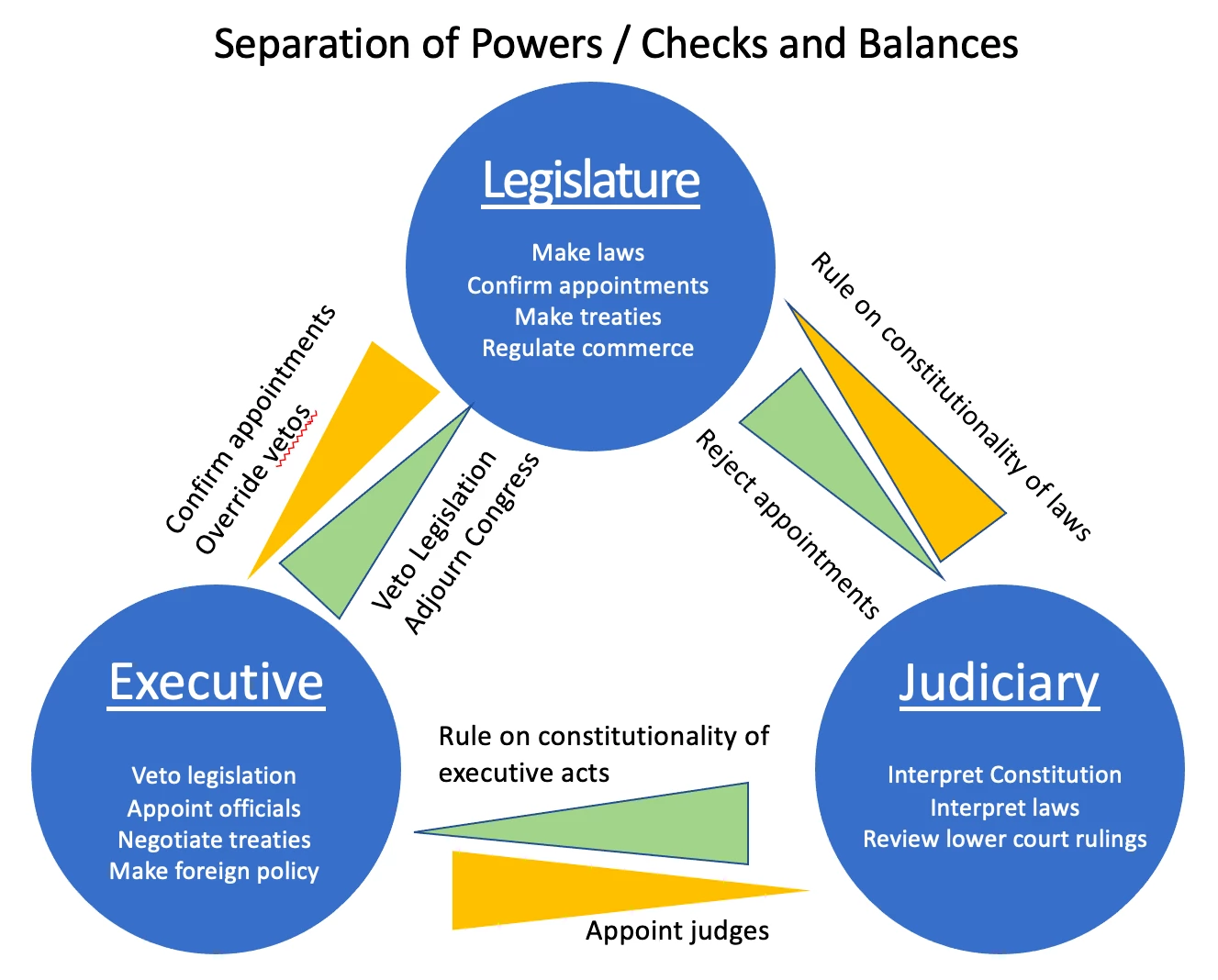
🧩 Separation of Powers
Power Is Divided, Not Centralized
The Constitution divides government into three distinct branches:
| Branch | Role |
|---|---|
| Legislative | Makes the laws |
| Executive | Enforces the laws |
| Judicial | Interprets the laws |
No branch may exercise the core powers of another.
Why It Matters
Concentrated power leads to tyranny. Divided power forces cooperation and restraint.
⚖️ Checks and Balances
Each Branch Limits the Others
Separation alone is not enough. Each branch has tools to check the others.
Examples
-
President vetoes laws
-
Congress overrides vetoes
-
Courts strike down unconstitutional laws
-
Senate confirms appointments
Why It Matters
No branch is supreme. Every action is subject to review.
🏛️ Federalism
Power Shared Between National and State Governments
The Constitution divides authority between:
-
Federal government
-
State governments
Some powers are national, some are state-based, and some are shared.
Why It Matters
Federalism:
-
Prevents over-centralization
-
Allows local governance
-
Encourages experimentation and diversity
States are not administrative units — they are sovereign partners.
📊 How the Principles Work Together
| Principle | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Popular Sovereignty | Legitimizes authority |
| Limited Government | Prevents abuse |
| Separation of Powers | Divides control |
| Checks & Balances | Enforces accountability |
| Federalism | Balances national & local power |
Together, these principles form a self-regulating system.
🧠 Case Study: When Power Is Challenged
Scenario
Congress passes a law. The President enforces it. A citizen challenges it in court.
What Happens?
-
Courts review the law
-
Constitutionality is examined
-
Law may be upheld or struck down
Lesson
No single institution has the final word unless the Constitution allows it.
❓ Quick Knowledge Check
1. What does “popular sovereignty” mean?
➡️ Government power comes from the people
2. Why is limited government important?
➡️ To prevent abuse of power
3. Why divide power into branches?
➡️ To avoid concentration of authority
4. What is the purpose of federalism?
➡️ To share power between national and state governments
✍️ Reader Reflection
Which constitutional principle do you believe is most important today, and why? We would love to hear your comments
🧾 Final Thoughts
The genius of the Constitution is not found in any single principle — but in how they work together. Power is granted, divided, restrained, and ultimately controlled by the people.
These principles are not abstract ideas. They shape every law, election, and court decision in the United States.
📌 Coming Next
The Preamble: Meaning, Purpose, and Promise



